up to 10% OFF!
What is a gallium nitride charger?
Recently, a new charging technology has entered our field of vision: gallium nitride (GaN). Its appearance has caused widespread discussion, and some people say that this is the perfect solution for future chargers.

Charger principle
Mobile phone chargers or laptop chargers are usually a switching power supply design. We can see from the figure below that the transformer is the largest component in the charger. Therefore, the general high-power charger (65W/100W) has a relatively large volume and is not easy to carry. A good way is to increase the switching frequency of the switch transistor, which can reduce the size of the transformer.
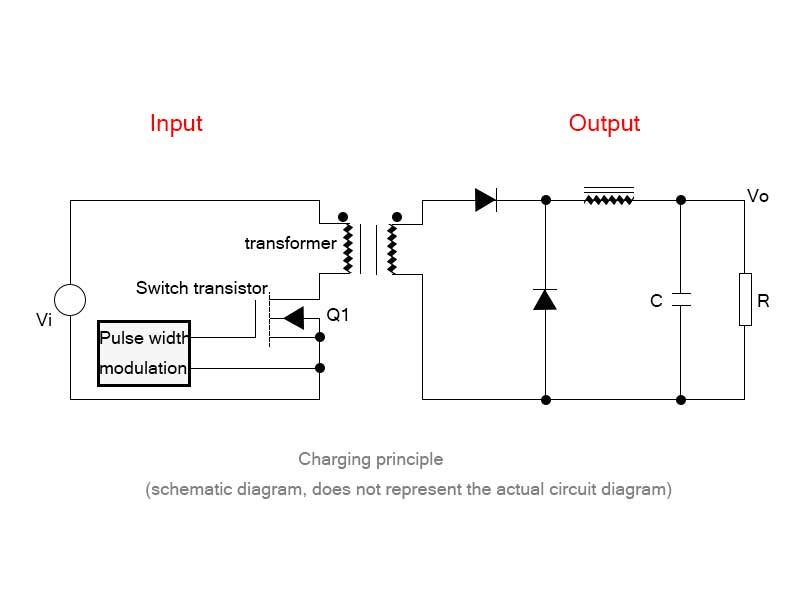
At present, the switch transistors are made of semiconductor materials such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge). However, the development of silicon has reached a bottleneck, and there is no room for improvement in the frequency of MOSFET switch transistors. Many manufacturers began to look for suitable substitutes.
Gallium nitride charger
Gallium nitride (GaN) is a direct energy gap semiconductor. Compared with Si, GaN has the advantages of large forbidden band width, strong breakdown ability, high thermal conductivity, high temperature resistance, and radiation resistance. The switch transistor uses GaN material to greatly increase the switching frequency and reduce the loss. In this way, the charger can use a smaller transformer and other inductive components. This is why the GaN charger has more power but can maintain a small size.
Switching power supplies include EMI, rectification and filtering, PWM control, switch transistors, transformers, synchronous rectification, feedback and output filtering. Therefore, miniaturization of the charger depends on many factors. The addition of GaN new materials has indeed brought improvements, but manufacturing technology and integration technology are equally important.
